Table of Contents
To keep your passwords private and safe from cybercriminals, follow the tips below:
1. Length Matters

Aim for a minimum of 12 characters. Longer passwords are generally more secure. Decide a memorable sentence infused with personal details rather than attempting to recall a complex combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. For instance, share something like “Duke, my dog, loves to play ball.” Infusing personal elements into your passphrase enhances memorability while maintaining a robust level of security. Make sure your passphrase is at least seven words long. The longer your passphrase, the more difficult it will be for someone to decipher.
2. Use a Mix of Characters

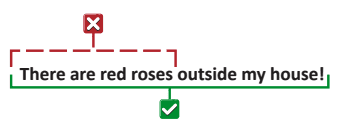
Include a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. This makes your password more complex and harder to guess.
3. Don't Use Any Common, Simple, Or Known Phrases

Avoid using common phrases or quotes, as these are easily guessable by hackers. Similarly, don’t use easily accessible personal information like your birthdate, your or your children’s names, or even your pet’s name. Also, steer clear of simple patterns like “123456” or “password.” These are among the first combinations attackers try.
4. Use A Different Passphrase For Each Account
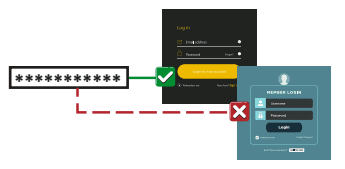
Employing the identical passphrase across various accounts increases the vulnerability of experiencing multiple breaches if that passphrase is compromised. This way, if one passphrase is compromised, your other accounts will be protected.
5. Use A Password Manager, Protected By A Strong Passphrase
Password managers are a secure way to generate and store complex passwords for you. You only need to remember one strong master passphrase.
6. Change Your Passphrase Regularly
Changing your passphrase periodically, especially for critical accounts, can help mitigate the risk if a password is compromised.
7. Make Sure You Use A Different Passphrase At Work Than You Do At Home
Ensure you utilize a distinct passphrase at your workplace compared to the one used at home. Similar to employing unique passphrases for individual accounts, using a different passphrase for work and personal accounts is crucial to your employer’s data security.
8. Make Sure That Your Accounts Lock For 15 Minutes After 5 Failed Login Attempts
Activating account lockouts following a specific number of unsuccessful login attempts is a crucial measure to safeguard your accounts against attacks. Ensure that your accounts are configured to initiate a lockout period of no less than 15 minutes after encountering 5 consecutive failed login attempts after encountering five consecutive failed attempts.
9. Enable Two-Factor Authentication

Adding an extra layer of security through Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) provides an additional barrier even if your password is compromised.
10. Check for Breaches

Periodically check if your email or passwords have been involved in any data breaches. Websites like “Have I Been Pwned” can provide this information.
Remember that creating a secure password is just one aspect of maintaining good cybersecurity hygiene. Regularly updating software, being cautious with emails and links, and staying informed about potential threats are also crucial for overall online security.
Should you encounter challenges with password management, are facing cybersecurity threats, or require assistance in fortifying your security measures, reach out to the experts at KT Connections for professional support.
